Variables:
Variables are nothing but reserved memory locations to store values. This means that when you create a variable you reserve some space in memory.
Python Variables:
- Variables are nothing but reserved memory locations to store values. This means that when you create a variable you reserve some space in memory.
- Based on the data type of a variable, the interpreter allocates memory and decides what can be stored in the reserved memory. Therefore, by assigning different data types to variables, you can store integers, decimals or characters in these variables
- Python variables do not need explicit declaration to reserve memory space. The declaration happens automatically when we assign a value to a variable. The equal sign (=) is used to assign values to variables.
Example code:
distance = 100 # Integer Assignment
cost = 99.6 # Floating Point Assignment
item = "Mango" # String Assignment
print distance
print cost
print item
OUTPUT:
100
99.6
Mango
Multiple Assignment of Variables:
- Python allows you to assign a single value to several variables simultaneously. For example −
x = y = z = 5
- Here, an integer object is created with the value 1, and all three variables are assigned to the same memory location. You can also assign multiple objects to multiple variables. For example
a, b, c = 1, 2, "Kaushal"
- Here, two integer objects with values 1 and 2 are assigned to variables a and b respectively, and one string object with the value "Kaushal" is assigned to the variable c.
Python Basic Operators:
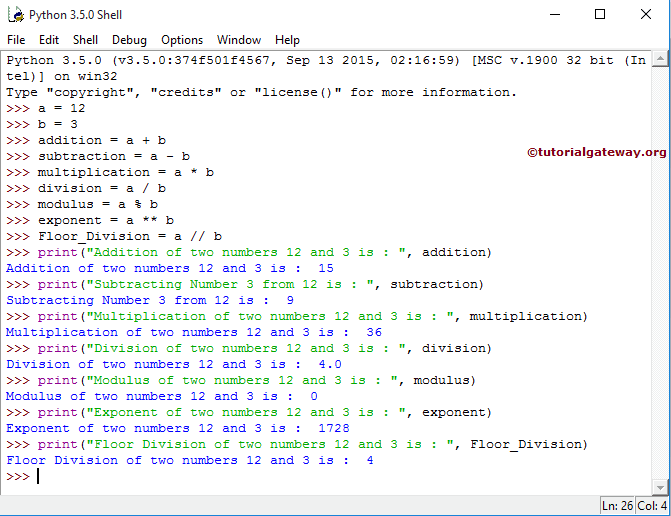
1. Python Arithmetic operators:

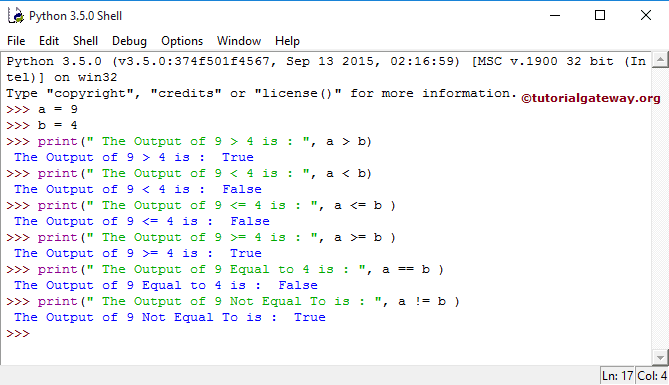
2. Python Comparison Operators:

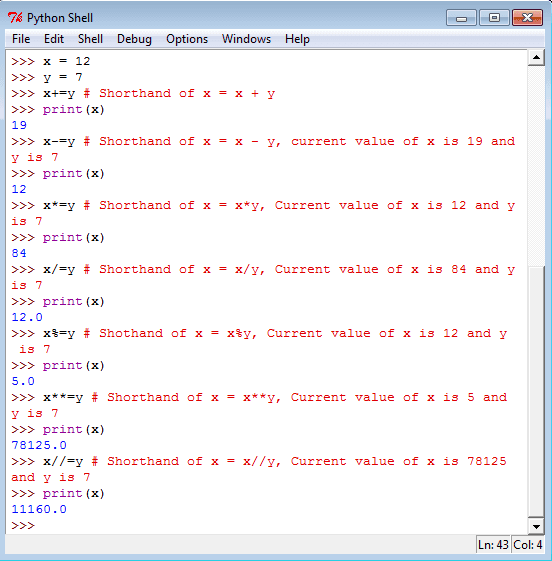
3. Python Assignment Operators:
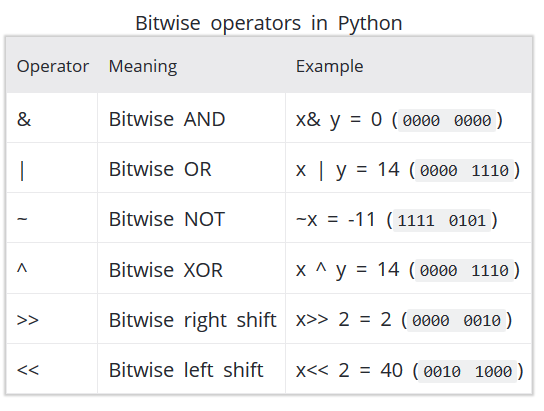
4. Python Bit wise Operators:
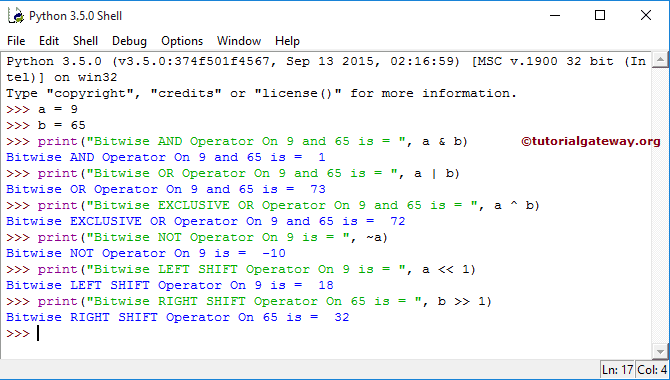
5. Python Logical Operators:

6. Python Membership Operators:


7. Python Identity Operators:



No comments:
Post a Comment